Job Execution Flow
Less than 1 minute
Job Execution Flow
Overview
- Nosana Jobs: Each job on the Nosana network is essentially an AI inference task that runs from a Docker container. The jobs are designed to utilize GPU resources efficiently.
- Nosana Nodes: Jobs run on different Nosana nodes, which are represented as Solana addresses in the Nosana explorer. Each node contributes its GPU resources to execute the jobs.
- GPU Markets: Different types of GPUs available in the network are categorized into various markets. Each market supports specific job requirements based on the type of GPU.
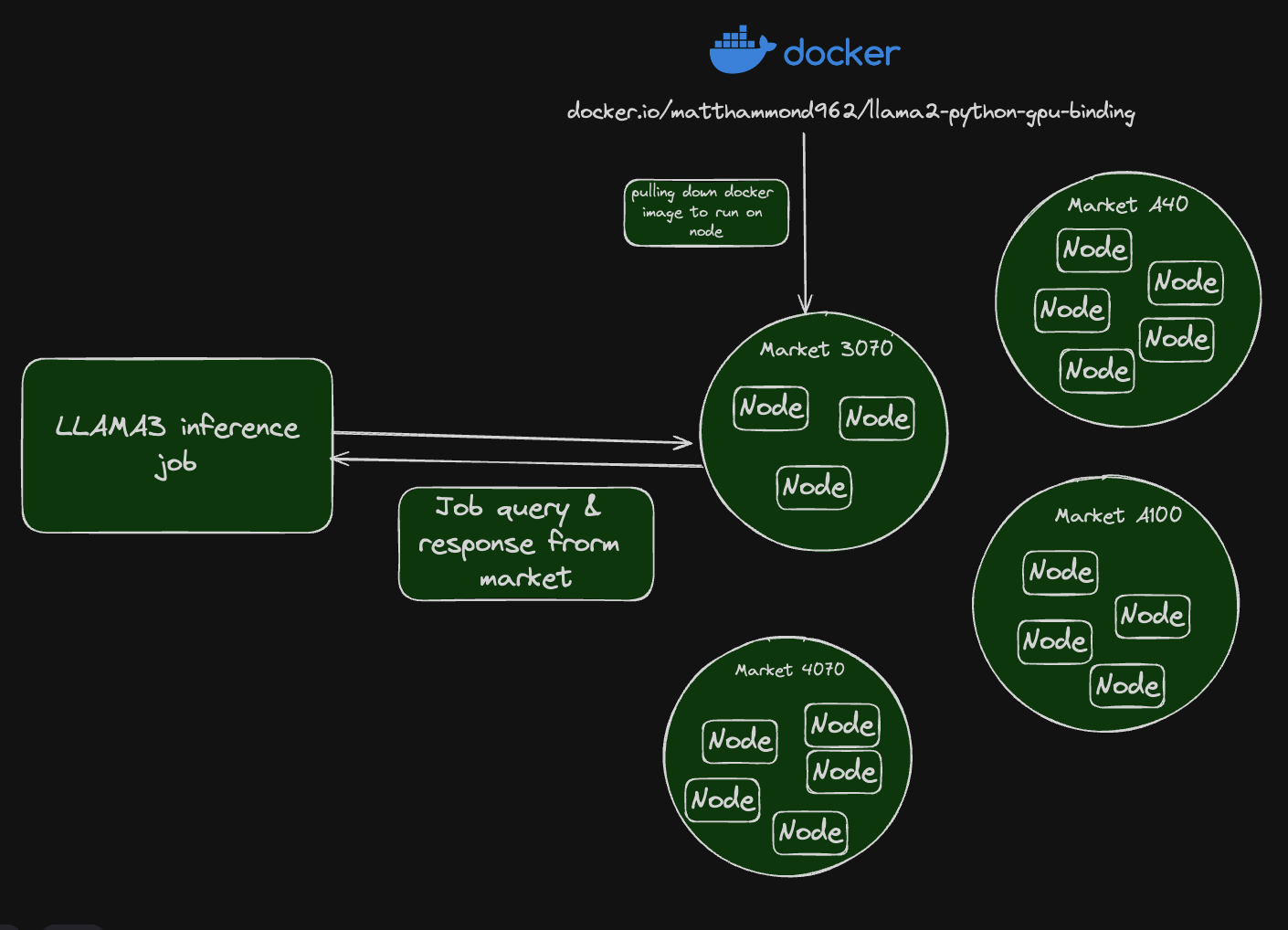
Execution Flow
These steps describe how submitting an inference job to the Nosana network.
- Job Submission: A user submits a job defined in a JSON format. This job specifies the tasks to be executed, the Docker images to be used, and whether GPU resources are required.
- Node Selection: The job is assigned to a Nosana node based on its requirements. The nodes are identified by their Solana addresses.
- Job Execution: The selected node pulls the necessary Docker image and executes the commands specified in the job. For example, running AI inference tasks using the provided Python scripts.
- Resource Utilization: Nodes utilize their GPU resources to run the tasks. This decentralized approach ensures efficient use of available hardware.
- Completion and Rewards: Once the job is completed, the node may earn $NOS tokens as a reward for contributing its GPU resources.
Examples
Nosana is a fully permissionless network, which means that whatever model you want to run in our network you can!
For examples you can take a look at the Examples Catalog or visit: Nosana Templates on GitHub.
Some examples of which models you can run and links can be found in the following table: